Chemical effects of electric current
Passage of current through chemical solutions causes chemical reactions to take place.
Chemical effects include:
- formation of gas bubbles at electrodes
- deposition of metals at electrodes
- Changes in solution colour
Electrolysis is the process by which ionic substances are decomposed into simpler substances when an electric current is passed through them.
Current Test – Conductors
Conductor
Any material that allows an electric current to pass through it is known as a conductor. Eg: metals like copper
Insulator (Bad Conductors)
Materials that do not allow the free flow of an electric current through it are known as bad conductors or insulators. E.g: Rubber, plastic.
Electric circuit
- A closed-loop path which a current take is known as an electric circuit.
- When the path of the circuit is closed, the current flows through it, but when there is a break in the path (switch is open) then, the circuit is open and, is not conducting.

Tester
A tester is a piece of electrical equipment used to check the presence of electric current. It is usually a conductor with a led/bulb to indicate that the current is present in the circuit.
Current – Conducting Liquids
Conducting Liquid
- Liquids conduct electricity too when there are salts dissolved in the liquid.
- Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of acids, bases or salts.
Acids, bases and salts
- Acids and bases are chemical substances that dissociate to form ions when dissolved in a solution. They are a good conductor of electricity because of the presence of the ions.
- Salts when dissolved in water also conduct as they release positive/negatively charged ions.
Conduction of electricity in the water
- Distilled water is a bad conductor of electricity because of the absence of dissolved salts and minerals.
- Water starts conducting when acids, bases or salts are dissolved that releases ions, which conduct when a potential difference is applied.
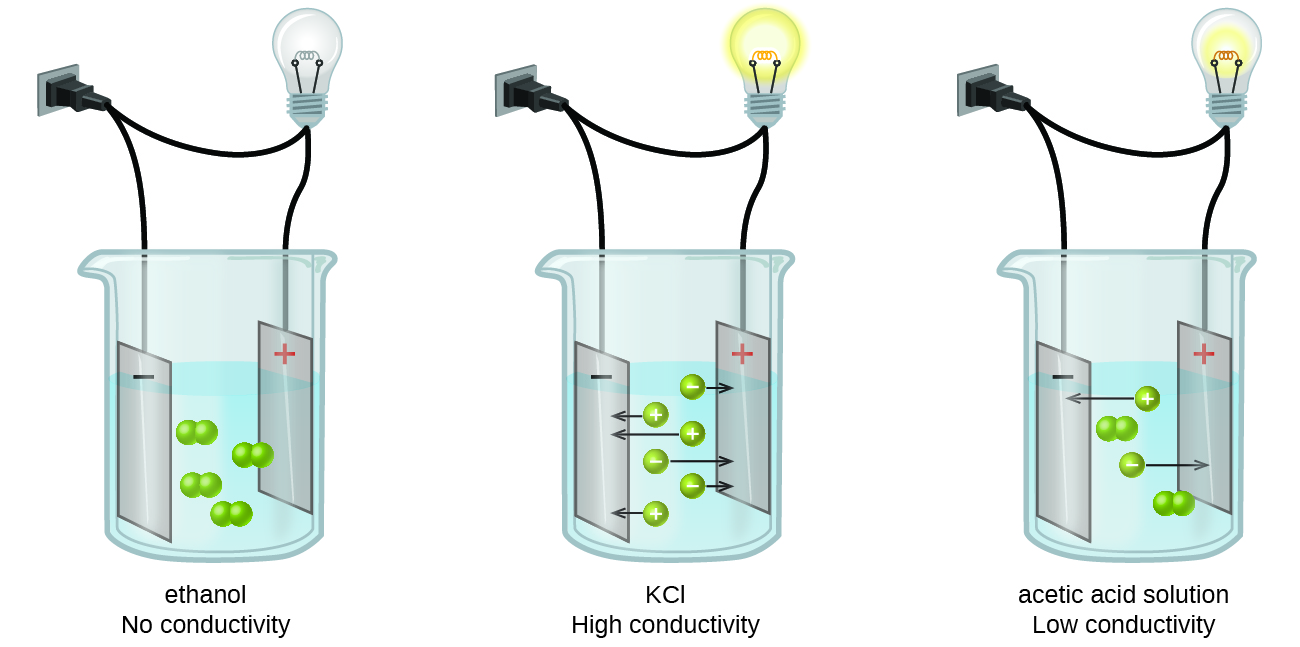
Electrodes and electrolyte
- A conductor, when immersed in a solution with its end connected to the terminals of a battery, thereby completing a circuit, is called as an electrode. There are usually 2 electrodes→ cathode(ve) and anode(+ve).
- An electrolyte is a solution in which the electrodes are submerged. They dissociate on the passage of electric current.
- The electrodes, electrolyte and the battery together form the electrochemical/electrolytic cell.
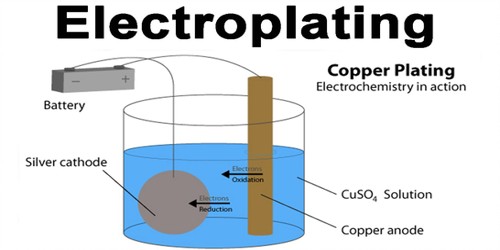
Electroplating
Electroplating
- The process of depositing a layer of desired metal on another material by means of electricity is known as electroplating.
- Example: Using Copper Sulphate solution as electrolyte and copper electrodes. Copper is electroplated on the negative electrode. The Cu in the solution is replenished due to the addition of copper ions from the positive electrode.
Applications of Electroplating
- Coating zinc on the iron to prevent corrosion and rust.
- Coating silver and gold for jewellery.
- Coating tin onto iron for cans as tin is less reactive than iron.
- Chromium coating for car parts, bath fittings as it has a shiny appearance.
Hope you like our work :)
For more chapters you can follow the link given below
For Link



Hello,
May I help you ?